I have seen many developers facing problem with version control system. I’ve worked on many projects and different git branching model.
In this blog post you will learn a successful git branching strategy and release management.
Let’s take a look on the below git branching and release flow -
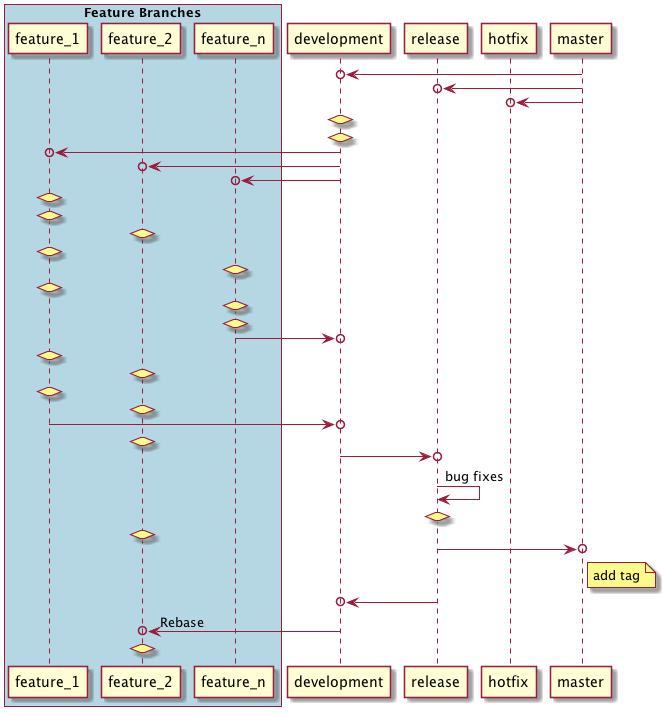
In the above flow -
- Development, release and hotfix branch fork from master.
- Every feature branch fork from development.
- Feature branch merge back to development.
- Development branch merge to release branch.
- Bug fixing while testing done in release branch.
- Release branch merge to master. (master branch will go to production.)
- Add tag for release on master branch.
- Release branch merge to development.
- Rebase all feature branches those are not in master.
In case of hotfix on production, use below flow -
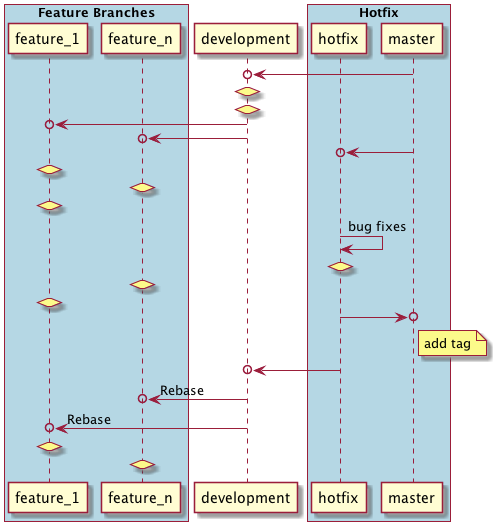
In the above hotfix flow -
- Fork hotfix branch from master
- Fix bug in hotfix branch
- Merge hotfix to master
- Add tag for hotfix
- Merge hotfix to development
- Rebase all feature branch those are not in master.
Commands used for this strategy.
- Fork new feature branch from development
$ git checkout development
$ git checkout -b feature_branch
OR
$ git checkout -b feature_branch development
- Merge feature branch to development
$ git checkout development
$ git merge --no-ff feature_branch
--no-ff is used for no fast forwarding, It will create a merge commit
rather then put all commit on development branch. This avoids losing
information about the historical existence of a feature branch.
- Adding tag
$ git tag -a 1.0.0 -m "Version 1.0.0 release"
-a for add
-m for message (optional)
You can also use the -s or -u <key> flags to sign your tag cryptographically.
- Rebase feature branches -
$ git checkout feature_branch
$ git rebase <source_branch/tag>
$ git push origin feature_branch
- Delete local feature branch
$ git branch -d feature_branch
It throws an error if the branch is not merged to any other branch.
If you need to delete an un-merged branch then use -D instead of -d.
Hope this helps
comments powered by Disqus